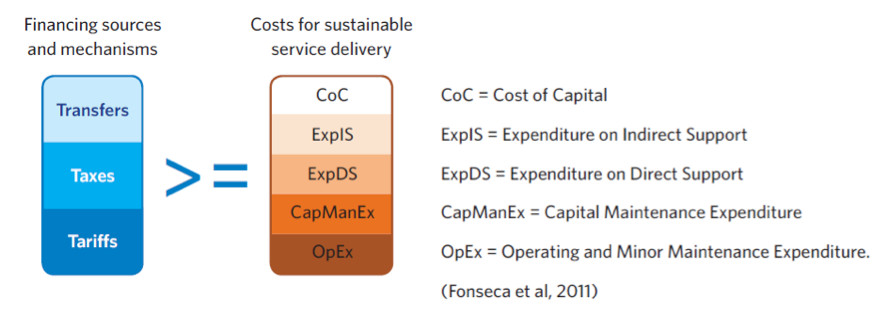
Financing Sources - Introduction
The main financing sources to recover the costs of water, sanitation and hygiene service delivery are (a combination of) taxes levied by national governments, transfers made by development partners and tariffs paid by users of a services (see figure 1). These financing sources in the water and sanitation sector are also known as the three Ts (e.g. taxes, transfers and tariffs).
Transfers refer to funds from international donors and charitable foundations (including NGOs, decentralized cooperation or local civil society organizations) that typically come from other countries (GLAAS, 2012). These funds can be contributed in the form of grants, concessionary loans (i.e. loans that include a “grant” element in the form of a subsidized interest rate or a grace period) or guarantees.
Tariffs are funds contributed by users of W water, sanitation and hygiene services for obtaining the service (GLAAS, 2012). Users generally make payments to service providers for getting access to the service and for using the service. When the service is self-provided (e.g. when a household builds and operates its own household latrine), the equity invested by the household (in the form of cash, material or time, sometimes referred to as “sweat equity”) would also fall under tariffs.
Taxes refer to funds originating from domestic taxes that are channelled to the sector via transfers from all levels of government; including national, regional and local (GLAAS, 2012). Such funds would typically be provided as subsidies, for capital investment or operations. “Hidden” forms of subsidies may include tax rebates, soft loans (i.e. loans at a subsidized interest rate) or subsidized services (e.g. subsidized electricity).
Links
- IRC International Water and Sanitation Centre is a knowledge broker, innovator and catalyst of change within the water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) sector working internationally and in selected focus countries and regions. IRC seeks to extend WASH services to the less privileged, while ensuring that services are based on the sustainable use of water resources, are appropriately managed, and are better governed. IRC works in partnership with governments, the public and private sector, Dutch and international organisations, UN institutions, development banks and non-governmental networks and organisations. For more information see www.irc.nl and www.irc.nl/financing
- Global Analysis and Assessment of Sanitation and Drinking-Water (GLAAS) is produced every two years by the World Health Organization (WHO) on behalf of UN-Water. It provides a global update on the policy frameworks, institutional arrangements, human resource base, and international and national finance streams in support of sanitation and drinking-water. For more information see [who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/glaas_report_2012/en/index.html.