Difference between revisions of "Powered pumps"
(→Pumps links) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
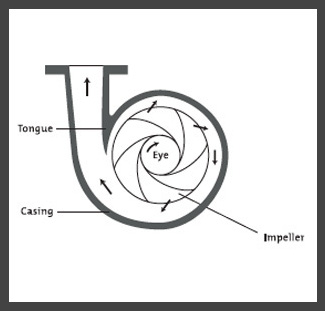
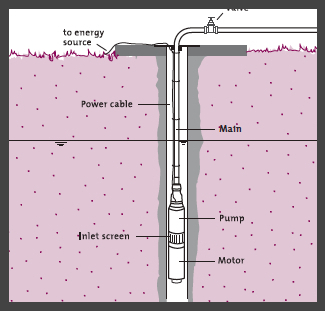
Powered pumps refer to pumps that are powered by sources such as: solar, animal, wind, diesel or biogas fuel, water, as well as suction, piston, centrifugal, and diaphragm technologies. The natural methods (wind and solar) are the most environmentally sustainable, yet may have greater initial costs. The hydraulic pump is both sustainable and inexpensive, yet must operate where a difference in water height occurs, e.g. mountainous areas. Some of the other pump technologies require specific maintenance that communities should be prepared for. Some pumps are better suited for community use and some for household use. Most pumps have depth limitations, so be sure to check how deep they can retrieve water. | Powered pumps refer to pumps that are powered by sources such as: solar, animal, wind, diesel or biogas fuel, water, as well as suction, piston, centrifugal, and diaphragm technologies. The natural methods (wind and solar) are the most environmentally sustainable, yet may have greater initial costs. The hydraulic pump is both sustainable and inexpensive, yet must operate where a difference in water height occurs, e.g. mountainous areas. Some of the other pump technologies require specific maintenance that communities should be prepared for. Some pumps are better suited for community use and some for household use. Most pumps have depth limitations, so be sure to check how deep they can retrieve water. | ||
<small-title /> | <small-title /> | ||
| − | <div style=" background-color: #efefef; text-align: center; -moz-border-radius: 2px; -webkit-border-radius: 2px; border: | + | <div style=" background-color: #efefef; text-align: center; -moz-border-radius: 2px; -webkit-border-radius: 2px; border: 5px solid #dedede; padding: 5px;" > |
| − | {|cellpadding=" | + | {|cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" width="100%" |
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="5" style="background-color:#efefef;"| | |colspan="5" style="background-color:#efefef;"| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:Horse_and_wind_powered_pumps.PNG|center|100px|link=Horse and wind powered pumps]] | |
| − | + | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:Fuel_efficient_motor_pump.PNG|center|100px|link=Small and efficient motor pumps]] | |
| − | + | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:SolarPump.jpg|center|100px|link=Solar powered pumps]] | |
| − | + | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:dieselGenerator.jpg|center|100px|link=Diesel generator pump]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:Horse_and_wind_powered_pumps.PNG|center| | ||
| − | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:Fuel_efficient_motor_pump.PNG|center| | ||
| − | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:SolarPump.jpg|center| | ||
| − | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:dieselGenerator.jpg|center| | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#efefef;"|<div class="center" style="width:auto; margin-left:auto; margin-right:auto;">[[Horse_and_wind_powered_pumps|Horse and wind <br>powered pumps]]</div> | |style="background:#efefef;"|<div class="center" style="width:auto; margin-left:auto; margin-right:auto;">[[Horse_and_wind_powered_pumps|Horse and wind <br>powered pumps]]</div> | ||
| Line 27: | Line 22: | ||
|colspan="5" style="background-color:#efefef;"| | |colspan="5" style="background-color:#efefef;"| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:CentrifugalPump.jpg|center|100px|link=Centrifugal pump]] | |
| − | + | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:SubmersiblePumpDiagram.jpg|center|100px|link=Submersible pump]] | |
| − | + | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:HydraulicRamPump.jpg|center|100px|link=Hydraulic Ram pump]] | |
| − | + | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:biogas fueled pump.jpg|center|100px|link=Biogas-fueled pump]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:CentrifugalPump.jpg|center| | ||
| − | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:SubmersiblePumpDiagram.jpg|center| | ||
| − | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:HydraulicRamPump.jpg|center| | ||
| − | |style="background:#efefef;"|[[Image:biogas fueled pump.jpg|center| | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#efefef;"|<div class="center" style="width:auto; margin-left:auto; margin-right:auto;">[[Centrifugal pump]]</div> | |style="background:#efefef;"|<div class="center" style="width:auto; margin-left:auto; margin-right:auto;">[[Centrifugal pump]]</div> | ||
Revision as of 03:51, 20 December 2014
Powered pumps refer to pumps that are powered by sources such as: solar, animal, wind, diesel or biogas fuel, water, as well as suction, piston, centrifugal, and diaphragm technologies. The natural methods (wind and solar) are the most environmentally sustainable, yet may have greater initial costs. The hydraulic pump is both sustainable and inexpensive, yet must operate where a difference in water height occurs, e.g. mountainous areas. Some of the other pump technologies require specific maintenance that communities should be prepared for. Some pumps are better suited for community use and some for household use. Most pumps have depth limitations, so be sure to check how deep they can retrieve water.
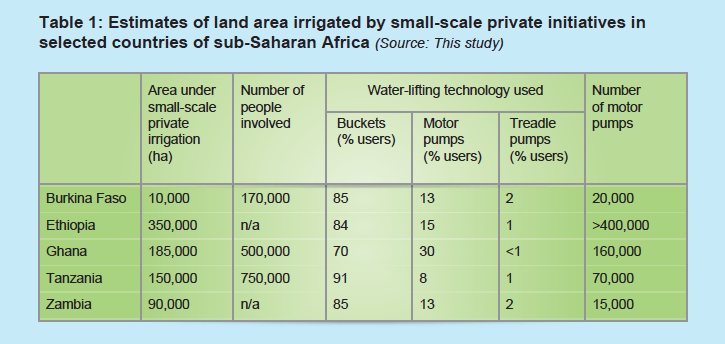
Small land owners and how they lift water in Africa
Pumps links
 Facilities Ibbagamuwa school Sri Lanka |
Smallholder irrigation could change the lives of millions of people
Smallholder farmers in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia are increasingly using small-scale irrigation to cultivate their land. Individually owned and operated irrigation technologies improve yields, reduce risks associated with climate variability and increase incomes, allowing farmers to purchase food, health care and education. There is great potential for many more farmers to benefit from small-scale irrigation. This report presents governments, donors, lending institutions, the private sector and farmers with the opportunity to make well-informed decisions about investments in agricultural water management (AWM) that could change the lives of millions of rural people.
- Water for wealth and food security: Supporting farmer-driven investments in agricultural water management. 2012 study by AgWater Solutions.