Difference between revisions of "वाटर पोर्टल / वर्षाजल संचयन / भूजल पुनर्भरण / चेकडैम (गली प्लग)"
(→संदर्भ आभार) |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Language-box|english_link= Water Portal / Rainwater Harvesting / Groundwater recharge / Check dams (gully plugs) | french_link= Coming soon | spanish_link= Coming soon | hindi_link= वाटर पोर्टल/ वर्षाजल संचयन/ भूजल पुनर्भरण/ चेकडैम (गली प्लग) | malayalam_link= Coming soon | tamil_link= Coming soon | korean_link= Coming soon | chinese_link=攔沙壩(防砂壩) | indonesian_link= Coming soon | japanese_link= Coming soon }} | + | {{Language-box|english_link= Water Portal / Rainwater Harvesting / Groundwater recharge / Check dams (gully plugs) | french_link= Coming soon | spanish_link= Coming soon | hindi_link= वाटर पोर्टल / वर्षाजल संचयन / भूजल पुनर्भरण / चेकडैम (गली प्लग) | malayalam_link= Coming soon | tamil_link= Coming soon | korean_link= Coming soon | chinese_link=攔沙壩(防砂壩) | indonesian_link= Coming soon | japanese_link= Coming soon }} |
[[Image:check dams (gully plugs) icon.png|right|80px]] | [[Image:check dams (gully plugs) icon.png|right|80px]] | ||
| − | [[Image:check dam india.jpg|thumb|right|200px| | + | [[Image:check dam india.jpg|thumb|right|200px|वर्षाजल संरक्षण के लिए चेकडैम. एनएमडीसी हीरा खदान, पन्ना, मध्य प्रदेश. फोटो: [http://www.retailforsure.com/www/photogallery.php ग्रीनफील्ड ईको-साल्यूशन प्रा. लिमिटेड.]]] |
| − | + | '''चेकडैम''' छोटा, अस्थायी या स्थायी बांध है, जिसका निर्माण एक जल निकासी खाई, गली, स्वेल या चैनल के आसपास किया जा सकता है ताकि तूफान आने पर संघनित प्रवाह की गति को कम किया जा सके. वे बाढ़ के पानी के एक प्रकार के रूप में वर्गीकृत किये जा सकते हैं, बनिस्पत एक अपवाह संचयन तकनीक के. चेकडैम लकड़ी, पत्थर, मटर बजरी से भरे मिट्टी के बैग या ईंटों और सीमेंट से बनाया जा सकता है. इनका केन्या और भारत में व्यापक रूप से इस्तेमाल किया गया है. इन बांधों भी [[Water_Portal_/_Rainwater_Harvesting_/_Groundwater_recharge_/_Leaky_dams | रिसाव बांधों]] के रूप में बनाया जा सकता है. ऐसे डैम जो नदी के बेड पर मोटे रेत परिवहन ([[Water_Portal_/_Rainwater_Harvesting_/_Groundwater_recharge_/_Sand_dam | रेत बांधों]]) से बनाये जाते हैं, उपयोग होते-होते खत्म हो जाते हैं. ये संरचनाएं अपेक्षाकृत सस्ती होती हैं और 2-5 साल तक चलती हैं. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ===उपयुक्त परिस्थितियां=== | ||
| + | * प्राकृतिक अपवाह क्षेत्रों में लगाएँ. | ||
| + | * आसपास के क्षेत्र की मिट्टी में पर्याप्त रिसाव क्षमता जरूरी है. | ||
{| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" align="center" | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" align="center" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! width="50%" style="background:#efefef;" | | + | ! width="50%" style="background:#efefef;" | लाभ |
| − | ! style="background:#f0f8ff;" | | + | ! style="background:#f0f8ff;" | हानि |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | valign="top" | - | + | | valign="top" | - - पानी की गति धीमी हो जाती है, जो कटाव को कम कर देती है और बाढ़ के दौरान अवांछित गली निर्माण से बचाती है. <br> |
| − | - | + | - खाई डिजाइन आवश्यक नहीं है, सिर्फ मौजूदा गली जल निकासी पैटर्न का उपयोग करता है.<br> |
| − | - | + | - उथले कुओं के पुनर्भरण में सहायता कर सकते हैं.<br> |
| − | - | + | - भूजल में खारापन कम कर सकते हैं.<br> |
| − | - | + | - भूजल पुनर्भरण और तलछट बाहर को समाहित होने देता है. (तलछट प्रवाह को कम कर देता है)<br> |
| − | - | + | - लागत प्रभावी - ये बांध स्थानीय सामग्री का उपयोग करके बना सकते हैं.<br> |
| − | | valign="top" | - | + | | valign="top" | - अगर गलत तरीके से डिजाइन किया गया हो, तो मछलियां इस पार से उस पार नहीं हो पातीं.<br> |
| − | - | + | - इसमें गाद भर सकता है और रखरखाव की आवश्यकता हो सकती है.<br> |
| − | - | + | - गाद भरने की वजह से रिसाव के स्तर को धीमी किया जा सकता है.<br> |
| − | - | + | - अस्पष्ट प्रकार की भूमि को स्वामित्व वाली जमीन में बदला जा सकता है.<br> |
|} | |} | ||
| + | ===पर्यावरण परिवर्तन के लिए लचीलापन=== | ||
| + | [[Image:EthiopianGullyPlug.jpg|thumb|right|200px|अडागा लेम्ने वाटरशेड में रिहेबिलिटेटेड गली, ओक्सुम, टिग्रे प्रांत. फोटो: जोहान रॉकस्ट्राम.]] | ||
| + | ====सुखाड़==== | ||
| + | '''सूखे के प्रभाव :''' पैदावार में कमी.<br> | ||
| + | '''प्रभाव के मूल कारण :''' फसलों के लिए कम पानी.<br> | ||
| + | '''वाश प्रणाली के लचीलेपन को बढ़ाने के लिए :''' सूखा रोधी और तेजी से बढ़ने वाली फसलें; किसानों की आजीविका में विविधता. | ||
| − | + | सूखे के प्रबंधन पर अधिक जानकारी : [[Resilient WASH systems in drought-prone areas | प्रभावित क्षेत्रों में लचीला वॉश सिस्टम]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==== | + | ====बाढ़==== |
| − | + | तीव्र बारिश की घटनाओं के साथ यह देखना चाहिये कि चैकडैम अभी भी अपने केंद्र से ठीक से प्रवाहित हो रहा है. यदि ऐसा नहीं है, बांध उखड़ सकता है, अगर यह अप्रभावी हो जाये तो पुनर्निर्माण की आवश्यकता होगी. | |
| − | === | + | ===निर्माण, संचालन और रखरखाव=== |
| − | ''' | + | '''सीमेंट पर सामान्य सलाह ''': संरचनाओं और अस्तरों में (जैसे टैंक, बांधों, जलमार्ग, कुओं में) दरार पड़ने की एक आम वजह सीमेंट का मिश्रण तैयार करने और इसे लगाने की त्रुटियां हैं. सबसे पहले, यह जरूरी है कि केवल शुद्ध सामग्रियों का उपयोग किया जाये: स्वच्छ पानी, स्वच्छ रेत, स्वच्छ चट्टान. सामग्री को बहुत अच्छी तरह से मिश्रित किया जाना चाहिये. दूसरी बात, मिश्रण बनाते वक्त कम से कम पानी की मात्रा का इस्तेमाल किया जाना चाहिये : कंक्रीट या सीमेंट भी सिर्फ काम के लायक होने चाहिये, सिर्फ सूखे किनारे पर तरल पर नहीं. तीसरा, सूखते वक्त सीमेंट या कंकरीट पर हमेशा नमी रहनी चाहिये, कम से कम एक सप्ताह के लिए. संरचनाओं को प्लास्टिक, बड़े पत्ते या अन्य सामग्री के साथ ढकना चाहिये और नियमित रूप से गीला रखा जाना चाहिए. |
| − | ''' | + | '''विशेष सलाह''': |
| − | [[Image:CementCheckDam.jpg|thumb|right|200px| | + | [[Image:CementCheckDam.jpg|thumb|right|200px|रेखांकन [http://www.saiplatform.org/uploads/Modules/Library/SAI%20Technical%20Brief%205%20%20The%20Importance%20of%20Soil%20to%20Water%20Use.pdf रेखांकन : जल संरक्षण तकनीकी सारांश.] एसएआई.]] |
| − | [[Image:WoodenCheckDam.jpg|thumb|right|200px| | + | [[Image:WoodenCheckDam.jpg|thumb|right|200px|लकड़ी के चैक डैम का क्रास सेक्सन. "टोंटी डालना" शामिल किया जाना चाहिए. <br> रेखांकन: [http://www.saiplatform.org/uploads/Modules/Library/SAI%20Technical%20Brief%205%20%20The%20Importance%20of%20Soil%20to%20Water%20Use.pdfरेखांकन : जल संरक्षण तकनीकी सारांश.] एसएआई.]] |
| − | + | चैकडैम का किनारा हमेशा बांध के केंद्र से ऊंचा होना चाहिये, ताकि पानी हमेशा बीच की तरफ प्रवाहित होती रहे (इस प्रवाह से बांध बचा रह जाता है). | |
| − | + | बांध भूमि की सतह में प्राकृतिक गलीज में अस्थायी या स्थायी सामग्री के बनाये जा सकते हैं. इसमें कंक्रीट, पृथ्वी, वनस्पति, पत्थर और झाड़-झंखाड़ आदि का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है. जहां मिट्टी का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है, संरचना के कटाव या विनाश से इसे बचा कर रखने की जरूरत होती है - यह करने के लिए, अक्सर एक ठोस स्पिलवे का निर्माण किया जाता है. जहां वे मौजूदा जल निकासी प्रणाली का उपयोग करते हैं, खाई की किसी डिजाइन की आवश्यकता नहीं होती (समोच्च खाइयों के साथ). | |
| − | + | बिना किसी विशिष्ट डिजाइन के जलवाहिनियों या स्थायी रूप से बह रही नदियों में चेकडैम का निर्माण नहीं किया जाना चाहिये (क्योंकि मछलियों के पार होने का रास्ता होना चाहिये). | |
| − | ==== | + | ====जल निकासी==== |
| − | * | + | * प्रवेश करने वाला जल अगले साल तक मिट्टी में नमी को बरकरार रखता है और फसलों की खेती में मददगार होता है. |
| − | * | + | * पंप सिंचाई के लिए पानी का सीधे इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. |
| − | * | + | * जल उथले कुओं और बोरबेल से लिया जा सकता है |
| − | ==== | + | ====रख-रखाव==== |
| − | + | चेकडैम हर बार पर्याप्त वर्षा के बाद तलछट संचय के मद्देनजर नियमित निरीक्षण किया जाना चाहिए. जब तलछट मूल ऊंचाई के आधे तक या उसके आसपास पहुंच जाये तो उसकी सफाई की जानी चाहिये. जांच कर यह सुनिश्चित कर लेना चाहिये कि प्रवाह बांध के केंद्र पर है, इसके नीचे या आसपास नहीं. जांच लें कि मुहाने में कोई कटाव तो नहीं है. | |
| − | === | + | ===लागत=== |
| − | + | अस्थायी बांधों के लिए (झाड़ियों की लकड़ी, पत्थर, मिट्टी से बने) भारत में लागत 200-400 अमेरिकी डॉलर और स्थायी बांधों के लिए (पत्थर, ईंट, सीमेंट से बने) 1,000 से 3,000 अमेरिकी डॉलर बताये जाते हैं, जो उनकी लंबाई और ऊंचाई पर निर्भर हैं. सामग्री के इस्तेमाल और गली के आकार के आधार पर लागत घट या बढ़ सकती है. | |
| − | 3,000 | ||
| − | === | + | ===जमीनी अनुभव=== |
| − | + | इथियोपिया में, भूमि स्वामित्व की अस्पष्टता की वजह से गलीज में फसल के प्रगतिशील परित्याग के लिए प्रेरित होते हैं. देखें : फॉकेममार्क, एम.; फॉक्स, पी.; पेरसन, जी.; रॉकस्ट्रॉम, जे (2001) [http://www.sswm.info/sites/default/files/reference_attachments/FALKENMARK%20et%20al%202001%20Water%20Harvesting%20for%20Upgrading%20of%20Rainfed%20Agriculture.pdf वर्षा आधारित कृषि के उन्नयन के लिए जल संचयन. समस्या विश्लेषण और अनुसंधान की जरूरत है]. स्टॉकहोम इंटरनेशनल वाटर इंस्टीच्यूट. | |
| − | === | + | ===नियमावली, वीडियो और लिंक=== |
| − | * [http://www.fao.org/docrep/W7314E/w7314e0q.htm | + | * [http://www.fao.org/docrep/W7314E/w7314e0q.htm टेक्नोलॉजीज फॉर वाटर हारवेस्टिंग एंड स्वाइल मॉइश्चर कंजर्वेशन इन स्माल वाटरशेड फॉर स्मॉल स्केल इरिगेशन], बाय आरके सिवनप्पन. |
| − | === | + | ===संदर्भ आभार=== |
| − | * | + | * केयर नीदरलैंड, डेस्क स्टडी : [[Resilient WASH systems in drought-prone areas | रिसिलियेंट वॉश सिस्टम इन ड्राउट प्रोन एरियाज]]. अक्टूबर 2010. |
| − | * | + | * रुफिनो, एल, [http://www.saiplatform.org/uploads/Library/Technical%20Brief%202%20%20Rainwater%20harvesting%20%20artificial%20recharge%20to%20groundwater.pdf वाटर कंजर्वेशन टेक्निकल ब्रीफ : टीबी 2 – रेनवाटर हार्वेस्टिंग एंड आर्टिफिशियल रिचार्ज टू ग्राउंडवाटर]. सस्टेनेबल एग्रीकल्चर इनिशियेटिव(साई). अगस्त 2009. |
Latest revision as of 03:20, 12 January 2016
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

चेकडैम छोटा, अस्थायी या स्थायी बांध है, जिसका निर्माण एक जल निकासी खाई, गली, स्वेल या चैनल के आसपास किया जा सकता है ताकि तूफान आने पर संघनित प्रवाह की गति को कम किया जा सके. वे बाढ़ के पानी के एक प्रकार के रूप में वर्गीकृत किये जा सकते हैं, बनिस्पत एक अपवाह संचयन तकनीक के. चेकडैम लकड़ी, पत्थर, मटर बजरी से भरे मिट्टी के बैग या ईंटों और सीमेंट से बनाया जा सकता है. इनका केन्या और भारत में व्यापक रूप से इस्तेमाल किया गया है. इन बांधों भी रिसाव बांधों के रूप में बनाया जा सकता है. ऐसे डैम जो नदी के बेड पर मोटे रेत परिवहन ( रेत बांधों) से बनाये जाते हैं, उपयोग होते-होते खत्म हो जाते हैं. ये संरचनाएं अपेक्षाकृत सस्ती होती हैं और 2-5 साल तक चलती हैं.
Contents
उपयुक्त परिस्थितियां
- प्राकृतिक अपवाह क्षेत्रों में लगाएँ.
- आसपास के क्षेत्र की मिट्टी में पर्याप्त रिसाव क्षमता जरूरी है.
| लाभ | हानि |
|---|---|
| - - पानी की गति धीमी हो जाती है, जो कटाव को कम कर देती है और बाढ़ के दौरान अवांछित गली निर्माण से बचाती है. - खाई डिजाइन आवश्यक नहीं है, सिर्फ मौजूदा गली जल निकासी पैटर्न का उपयोग करता है. |
- अगर गलत तरीके से डिजाइन किया गया हो, तो मछलियां इस पार से उस पार नहीं हो पातीं. - इसमें गाद भर सकता है और रखरखाव की आवश्यकता हो सकती है. |
पर्यावरण परिवर्तन के लिए लचीलापन
सुखाड़
सूखे के प्रभाव : पैदावार में कमी.
प्रभाव के मूल कारण : फसलों के लिए कम पानी.
वाश प्रणाली के लचीलेपन को बढ़ाने के लिए : सूखा रोधी और तेजी से बढ़ने वाली फसलें; किसानों की आजीविका में विविधता.
सूखे के प्रबंधन पर अधिक जानकारी : प्रभावित क्षेत्रों में लचीला वॉश सिस्टम.
बाढ़
तीव्र बारिश की घटनाओं के साथ यह देखना चाहिये कि चैकडैम अभी भी अपने केंद्र से ठीक से प्रवाहित हो रहा है. यदि ऐसा नहीं है, बांध उखड़ सकता है, अगर यह अप्रभावी हो जाये तो पुनर्निर्माण की आवश्यकता होगी.
निर्माण, संचालन और रखरखाव
सीमेंट पर सामान्य सलाह : संरचनाओं और अस्तरों में (जैसे टैंक, बांधों, जलमार्ग, कुओं में) दरार पड़ने की एक आम वजह सीमेंट का मिश्रण तैयार करने और इसे लगाने की त्रुटियां हैं. सबसे पहले, यह जरूरी है कि केवल शुद्ध सामग्रियों का उपयोग किया जाये: स्वच्छ पानी, स्वच्छ रेत, स्वच्छ चट्टान. सामग्री को बहुत अच्छी तरह से मिश्रित किया जाना चाहिये. दूसरी बात, मिश्रण बनाते वक्त कम से कम पानी की मात्रा का इस्तेमाल किया जाना चाहिये : कंक्रीट या सीमेंट भी सिर्फ काम के लायक होने चाहिये, सिर्फ सूखे किनारे पर तरल पर नहीं. तीसरा, सूखते वक्त सीमेंट या कंकरीट पर हमेशा नमी रहनी चाहिये, कम से कम एक सप्ताह के लिए. संरचनाओं को प्लास्टिक, बड़े पत्ते या अन्य सामग्री के साथ ढकना चाहिये और नियमित रूप से गीला रखा जाना चाहिए.
विशेष सलाह:
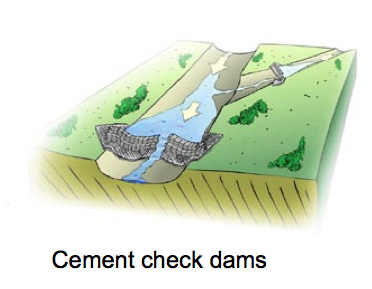
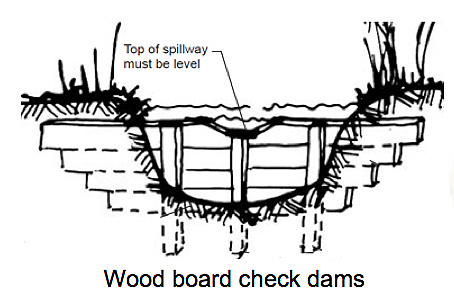
रेखांकन: : जल संरक्षण तकनीकी सारांश. एसएआई.
चैकडैम का किनारा हमेशा बांध के केंद्र से ऊंचा होना चाहिये, ताकि पानी हमेशा बीच की तरफ प्रवाहित होती रहे (इस प्रवाह से बांध बचा रह जाता है).
बांध भूमि की सतह में प्राकृतिक गलीज में अस्थायी या स्थायी सामग्री के बनाये जा सकते हैं. इसमें कंक्रीट, पृथ्वी, वनस्पति, पत्थर और झाड़-झंखाड़ आदि का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है. जहां मिट्टी का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है, संरचना के कटाव या विनाश से इसे बचा कर रखने की जरूरत होती है - यह करने के लिए, अक्सर एक ठोस स्पिलवे का निर्माण किया जाता है. जहां वे मौजूदा जल निकासी प्रणाली का उपयोग करते हैं, खाई की किसी डिजाइन की आवश्यकता नहीं होती (समोच्च खाइयों के साथ).
बिना किसी विशिष्ट डिजाइन के जलवाहिनियों या स्थायी रूप से बह रही नदियों में चेकडैम का निर्माण नहीं किया जाना चाहिये (क्योंकि मछलियों के पार होने का रास्ता होना चाहिये).
जल निकासी
- प्रवेश करने वाला जल अगले साल तक मिट्टी में नमी को बरकरार रखता है और फसलों की खेती में मददगार होता है.
- पंप सिंचाई के लिए पानी का सीधे इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है.
- जल उथले कुओं और बोरबेल से लिया जा सकता है
रख-रखाव
चेकडैम हर बार पर्याप्त वर्षा के बाद तलछट संचय के मद्देनजर नियमित निरीक्षण किया जाना चाहिए. जब तलछट मूल ऊंचाई के आधे तक या उसके आसपास पहुंच जाये तो उसकी सफाई की जानी चाहिये. जांच कर यह सुनिश्चित कर लेना चाहिये कि प्रवाह बांध के केंद्र पर है, इसके नीचे या आसपास नहीं. जांच लें कि मुहाने में कोई कटाव तो नहीं है.
लागत
अस्थायी बांधों के लिए (झाड़ियों की लकड़ी, पत्थर, मिट्टी से बने) भारत में लागत 200-400 अमेरिकी डॉलर और स्थायी बांधों के लिए (पत्थर, ईंट, सीमेंट से बने) 1,000 से 3,000 अमेरिकी डॉलर बताये जाते हैं, जो उनकी लंबाई और ऊंचाई पर निर्भर हैं. सामग्री के इस्तेमाल और गली के आकार के आधार पर लागत घट या बढ़ सकती है.
जमीनी अनुभव
इथियोपिया में, भूमि स्वामित्व की अस्पष्टता की वजह से गलीज में फसल के प्रगतिशील परित्याग के लिए प्रेरित होते हैं. देखें : फॉकेममार्क, एम.; फॉक्स, पी.; पेरसन, जी.; रॉकस्ट्रॉम, जे (2001) वर्षा आधारित कृषि के उन्नयन के लिए जल संचयन. समस्या विश्लेषण और अनुसंधान की जरूरत है. स्टॉकहोम इंटरनेशनल वाटर इंस्टीच्यूट.
नियमावली, वीडियो और लिंक
- टेक्नोलॉजीज फॉर वाटर हारवेस्टिंग एंड स्वाइल मॉइश्चर कंजर्वेशन इन स्माल वाटरशेड फॉर स्मॉल स्केल इरिगेशन, बाय आरके सिवनप्पन.
संदर्भ आभार
- केयर नीदरलैंड, डेस्क स्टडी : रिसिलियेंट वॉश सिस्टम इन ड्राउट प्रोन एरियाज. अक्टूबर 2010.
- रुफिनो, एल, वाटर कंजर्वेशन टेक्निकल ब्रीफ : टीबी 2 – रेनवाटर हार्वेस्टिंग एंड आर्टिफिशियल रिचार्ज टू ग्राउंडवाटर. सस्टेनेबल एग्रीकल्चर इनिशियेटिव(साई). अगस्त 2009.

