Difference between revisions of "Water Portal / Rainwater Harvesting / Surface water"
(→Field experiences) |
(→Field experiences) |
||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
===Field experiences=== | ===Field experiences=== | ||
| − | These projects | + | These projects may be utilizing surface water harvesting techniques and are part of the project listing in Really Simple Reporting (RSR) on [http://www.akvo.org Akvo.org]. |
{| style="width: 70%; text-align: justify; background-color: #f5f5f5;" | {| style="width: 70%; text-align: justify; background-color: #f5f5f5;" | ||
Revision as of 07:08, 17 October 2013
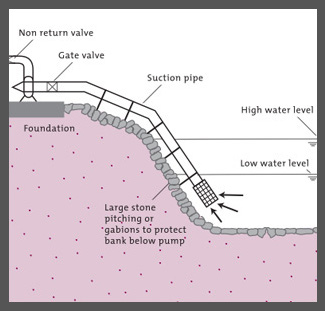
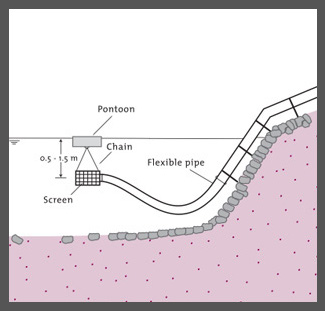
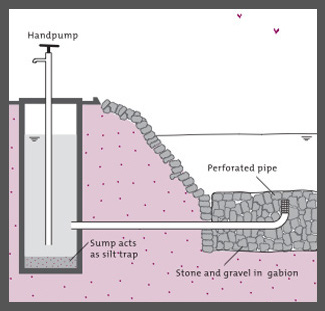
Rainwater that is not captured directly, used by agriculture, or absorbed into the ground becomes surface water. Surface water harvesting includes all systems that collect and conserve surface runoff after a rainstorm or in intermittent streams, rivers, or wetlands for storage in open ponds and reservoirs. This can provide water for direct household use (treatment is generally required), irrigation, livestock, and aquaculture. Storage can also be the goal of collecting surface water, whether through open reservoirs or direct infiltration to aquifers below ground. Storing water in an aquifer conserves water better as it prevents evaporation, unlike open reservoir systems.
Climate change considerations
Cement made for water collecting structures, in a time of drought, can be made poorly due to less (or polluted) water used in the cement-making process. Higher heat from climate change will increase evaporation rates in reservoirs, or floods may damage infrastructure and increase runoff volumes. These effects and more are listed and tips are given to adapt the water system to climate change conditions.
Field experiences
These projects may be utilizing surface water harvesting techniques and are part of the project listing in Really Simple Reporting (RSR) on Akvo.org.
| Akvo RSR Project: Ensure access to safe water and sanitation
Salinity, arsenic, lack of proper IWRM, and incidence of natural disasters in the three districts of the Southwest coastal belt of Bangladesh cause a lot of socioeconomic and health related problems. The programme is right-based and strengthens knowledge and capacity of community WASH groups as well as local government institutions. As problems are multifaceted, the programme uses a multi-pronged strategy and facilitates partnership with existing institutional stakeholders relevant for WASH sector. |
| Akvo RSR Project: Rwenzori Integrated School WASH Project
HEWASA and JESE will jointly implement this 3-years school WASH program in Kabarole district in the West of Uganda. Not only 24 schools will be supplied with WASH facilities (Rainwater Harvesting Tanks, Ecosan Latrines and Handwashing facilities) but 72 surrounding communities will be included for household latrine construction through CLTS, hygiene and health education and promotion. |
Surface water links
- Rainwater Harvesting and Utilisation. Blue Drop Series: Book 2: Beneficiaries & Capacity Builders. UN-HABITAT.
- CARE Nederland, Desk Study Resilient WASH systems in drought prone areas. October 2010.