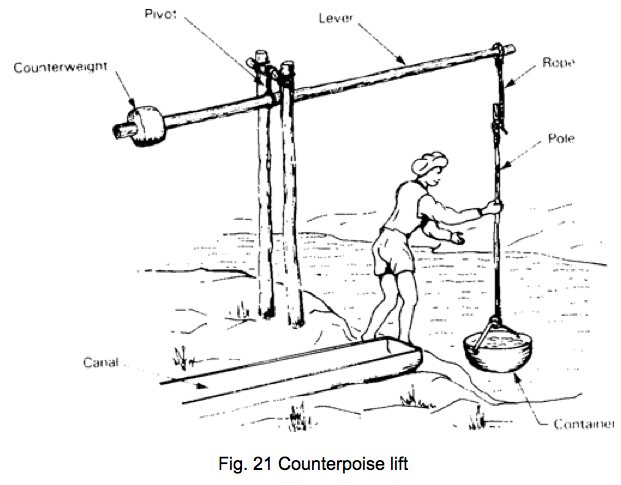
Counterpoise lift
| |
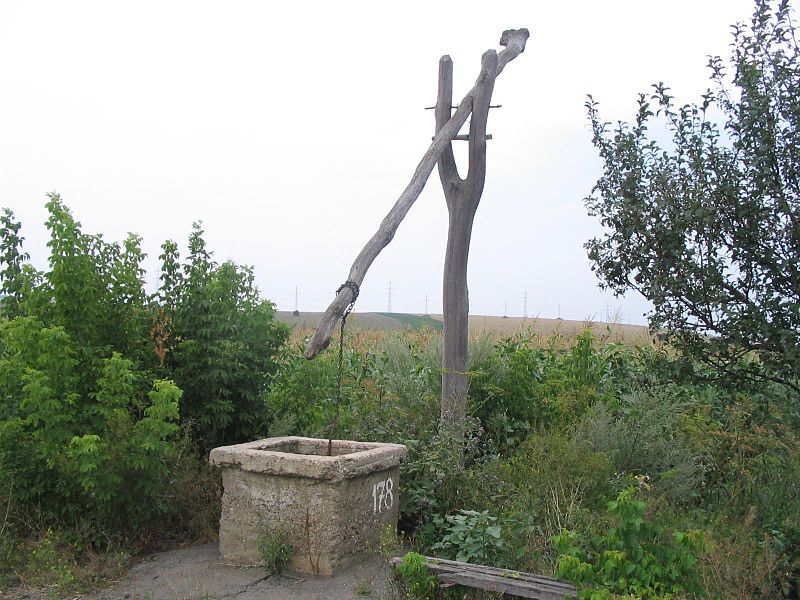


Also known as shadoof, shaduf, dhenkli or picottach, the counterpoise lift consists of a long wooden pole and is generally used for lifting water from unlined wells, streams or ponds and for irrigating small fields. A weight, often a large stone or a ball of dried mud or a basket filled with small stones is fixed at the shorter end of the pole to counterpoise the weight of a filled bucket which is attached to the longer arm of the pole with a rope. The bucket is emptied by a sideways tipping motion. This device is used to lift water up to a height of 1 - 3 metres. About 2000 litres of water can be lifted from the depth of 2 to 3 metres in one hour.
Don is also a similar type of device which is used in west Bengal and neighbouring areas to lift water up to a height of 1.2 meters. It consists of a boat shaped trough, closed at one end and open at the other, made of wood or galvanized iron sheets. The trough oscillates on a fixed centre and its closed end is alternately dipped into water and raised. The water flows into the field channel through the open end of the trough.
Reference manuals, videos, and links
- Video: Working Shaduf.
Acknowledgements
- Water lifting devices. Agricoop.nic.in
- Water lifting devices. Inseda.org