Promoting re-use of sanitation products
Contents
Introduction
Human faeces and urine contain a large amount of nutrients, which can be used in agriculture for crop irrigation, for fish aquaculture, or aquatic vegetable pond fertilization. In many cultures, for example the Chinese, the idea that 'waste is too valuable to waste' is well known, and has been practiced for centuries. In many other cultures however, sanitation products are hardly used for productive use, although interest is growing. Especially the 'Ecological Sanitation (EcoSan)' movement (also called 'sustainable sanitation') has led to more interest in this field. When sanitation products are reused, great care has to be given to dealing with the potential health and environmental risks of human waste products.
Large-scale sewerage-based systems have significant drawbacks. Enormous investments are needed, operating and maintenance costs are very high, the water consumption is very large, and a large volume of waste is produced which can be costly to treat. Especially in arid zones, the water use is a problem. A second problem is that in cities, all kinds of waste are disposed of in the sewer, leading to a very varied mixture which is difficult to process. Ecological sanitation can both be applied in cities (often in public toilet blocks), and in peri-urban and rural areas.
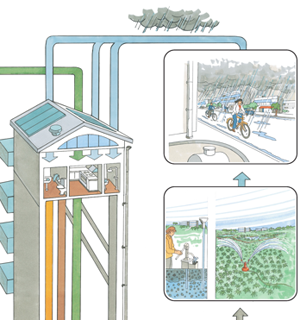
Description of Approach
Ecosan is not so much a technology as a way of thinking in which (treated) human excreta and greywater as a valuable resource, which can be used for productive use. In that sense, it needs a change of thinking about waste issues in terms of recycing and closing material loops, in which waste is not longer regarded as waste but as a resource.
Potential
In most conventional wastewater and sanitation systems, large amounts of valuable nutrients are wasted, which can lead to a reduction is soil fertility, or the need to apply (and buy) chemical fertilizer. Therefore, applying ecological sanitation has a very large potential.
Country Experiences
EcoSan is practiced in most world regions. EcoSanRes has a World Map with EcoSan initiatives.
Movies
External links
- Ecological Sanitation on Wikipedia, with many links
- EcoSanRes - Research on Econological Sanitation
- SuSanA - Sustainable sanitation for a better life. This website has interesting visual aids and technical drawings, and many links to studies on EcoSan in Africa.
- GTZ Ecological Sanitation pages
- Jackson, B. (2005). Review of EcoSan Experience in Eastern and Southern Africa. Water and Sanitation Program - The World Bank
- UNESCO-IHE online course on Ecological Sanitation
- Ecological Sanitation pages at WASTE
- Ecosan Services Foundation - non-profit Ecosan consultancy
- [http://www.reseaucrepa.org/page/319 EcoSan information from Centre Régional pour l'Eau Potable et
l'Assainissement à faible coût (CREPA) (in french)]
