Difference between revisions of "Surface Disposal and Storage"
(→References and external links) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {|style="float: left;" | |
| − | {{ | + | |{{Language-box|english_link=Surface Disposal and Storage|french_link=Mise_en_décharge|spanish_link=Disposición_final_en_Superficie|hindi_link=coming soon|malayalam_link=coming soon|tamil_link=coming soon | korean_link=coming soon | chinese_link=Coming soon | indonesian_link=Coming soon | japanese_link=Coming soon}} |
| + | |} | ||
| + | {|width="100%" | ||
| + | |style="width:50%;"|{{santable_new| | ||
sys1=[[Single Pit System|1]]| | sys1=[[Single Pit System|1]]| | ||
sys2=[[Waterless System with Alternating Pits|2]]| | sys2=[[Waterless System with Alternating Pits|2]]| | ||
| − | sys3=[[Pour Flush System | + | sys3=[[Pour Flush Pit System without Sludge Production|3]]| |
sys4=[[Waterless System with Urine Diversion|4]]| | sys4=[[Waterless System with Urine Diversion|4]]| | ||
| − | sys5=[[Blackwater Treatment System with Infiltration| | + | sys5=[[Biogas System|5]]| |
| − | + | sys6=[[Blackwater Treatment System with Infiltration|6]]| | |
| − | + | sys7=[[Blackwater Treatment System with Effluent Transport|7]]| | |
| − | + | sys8=[[Blackwater Transport to (Semi-) Centralized Treatment System|8]]| | |
| + | sys9=[[Sewerage System with Urine Diversion|9]]| | ||
pic=Surface_disposal.png| | pic=Surface_disposal.png| | ||
ApplHousehold=X| | ApplHousehold=X| | ||
| Line 16: | Line 20: | ||
ManShared=XX| | ManShared=XX| | ||
ManPublic=XX| | ManPublic=XX| | ||
| − | Input1= | + | Input1=Sludge |Input2=Pit Humus |Input3=Compost|Input4=Dry Cleansing Material|Input5= Dried Faeces|Input6=Pre-Treatment Products |
| − | Output1= | + | |Output1=None |Output2= | Output3= | Output4= | Output5= |
}} | }} | ||
| + | |[[Image:Surface_disposal.png |right|500px]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| − | [[Image:Icon_surface_disposal.png |right| | + | [[Image:Icon_surface_disposal.png |right|80px]] |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Surface disposal refers to the stockpiling of sludge, faeces or other materials that cannot be used elsewhere. Once the material has been taken to a surface disposal site, it is not used later. Storage refers to temporary stockpiling. It can be done when there is no immediate need for the material and a future use is anticipated, or when further pathogen reduction and drying is desired before application.''' | |
| − | + | This technology is primarily used for sludge, although it is applicable for any type of dry, unusable material. One application of surface disposal is the disposal of dry cleansing materials, such as toilet paper, corn cobs, stones, newspaper and/or leaves. These materials cannot always be included along with other water-based products in some technologies and must be separated. | |
| − | + | A rubbish bin should be provided beside the User Interface to collect the cleansing materials and menstrual hygiene materials. Dry materials can be burned (e.g., corn cobs) or disposed of along with the household waste. For simplicity, the remainder of this technology information sheet will be dedicated to sludge since standard solid waste practices are beyond the scope of this Compendium. | |
| + | When there is no demand for or acceptance of the beneficial use of sludge, it can be placed in monofills (sludge-only landfills) or heaped into permanent piles. Temporary storage contributes to further dehydration of the product and the die-off of pathogens before it is used. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Design Considerations=== | ||
| + | Landfilling sludge along with municipal solid waste (MSW) is not advisable since it reduces the life of a landfill, which has been specifically designed for the containment of more noxious materials. As opposed to more centralized MSW landfills, surface disposal sites can be situated close to where the sludge is treated, limiting the need for long transport distances. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The main difference between surface disposal and land application is the application rate. There is no limit to the quantity of sludge that can be applied to the surface since nutrient loads or agronomic rates are not a concern. Attention must be paid, however, to groundwater contamination and leaching. More advanced surface disposal systems may incorporate a liner and leachate collection system in order to prevent nutrients and contaminants from infiltrating the groundwater. Sites for the temporary storage of a product should be covered to avoid rewetting by rainwater and the generation of leachate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
{{procontable | pro= | {{procontable | pro= | ||
| − | - Can make use of vacant or abandoned land | + | - May prevent unmitigated disposal <br> |
| − | - | + | - Storage may render the product more hygienic <br> |
| + | - Can make use of vacant or abandoned land <br> | ||
| + | - Little operation skills or maintenance required <br> | ||
| + | - Low capital and operating costs | ||
| + | | con= | ||
| + | - Requires a large land area <br> | ||
| + | - Potential leaching of nutrients and contaminants into groundwater <br> | ||
| + | - Surface disposal hampers the beneficial use of a resource <br> | ||
| + | - Odours may be noticeable, depending on prior treatment <br> | ||
| + | - May require special spreading equipment | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | == | + | ===Appropriateness=== |
| + | Since there are no benefits gained from surface disposal, it should not be considered as a primary option. However, where sludge use is not easily accepted, the contained and controlled stockpiling of solids is far preferable to uncontrolled dumping. Storage may, in some cases, be a good option to further dry and sanitize a material and to generate a safe, acceptable product. Storage may also be required to bridge the gap between supply and demand. Surface disposal and storage can be practiced in almost every climate and environment, although they may not be feasible where there is frequent flooding or where the groundwater table is high. | ||
| − | + | ===Health Aspects/Acceptance=== | |
| + | If a surface disposal and storage site is protected (e.g., by a fence) and located far from the public, there should be no risk of contact or nuisance. The contamination of groundwater resources by leachate should be prevented by adequate siting and design. Care should be taken to protect the disposal or storage site from vermin and pooling water, both of which could exacerbate smell and vector problems. | ||
| − | == | + | ===Operation & Maintenance=== |
| + | Staff should ensure that only appropriate materials are disposed of at the site and must maintain control over the traffic and | ||
| + | hours of operation. Workers should wear appropriate protective clothing. | ||
| − | + | ===References and external links=== | |
| + | *Strande, L., Ronteltap, M. and Brdjanovic, D. (Eds.) (2014). [https://www.susana.org/en/knowledge-hub/resources-and-publications/library/details/3591 Faecal Sludge Management. Systems Approach for Implementation and Operation]. IWA Publishing, London, UK. (Detailed book compiling the current state of knowledge on all aspects related to FSM) | ||
| − | + | * U.S. EPA (1999). [https://www.epa.gov/biosolids/biosolids-generation-use-and-disposal-united-states Biosolids Generation, Use, and Disposal in the United States]. EPA-530/R-99-009. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D.C., US. | |
| − | + | * U.S. EPA (1994). [https://www.epa.gov/biosolids/plain-english-guide-epa-part-503-biosolids-rule A Plain English Guide to the EPA Part 503 Biosolids Rule]. EPA832-R-93-003. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D.C., US. | |
| − | ==Acknowledgements== | + | ===Acknowledgements=== |
{{:Acknowledgements Sanitation}} | {{:Acknowledgements Sanitation}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 21:18, 7 March 2021
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
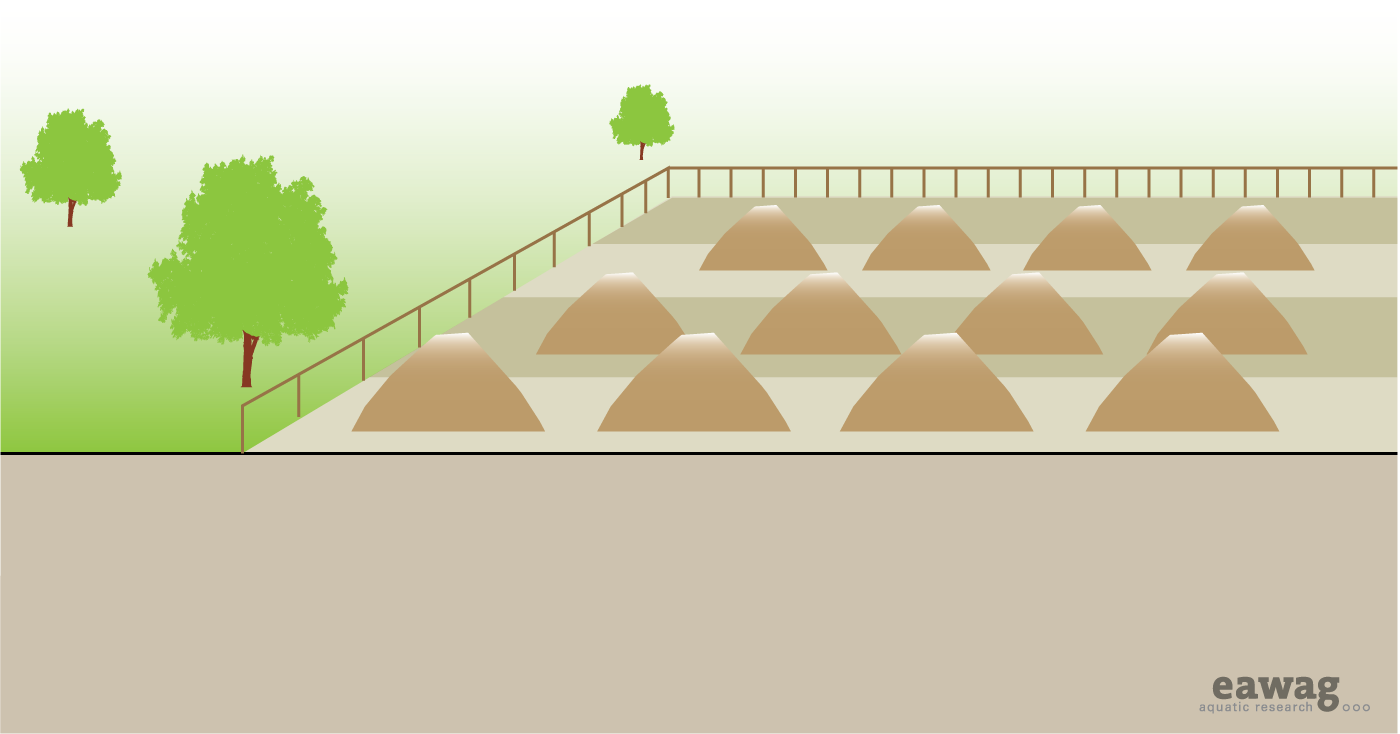
Surface disposal refers to the stockpiling of sludge, faeces or other materials that cannot be used elsewhere. Once the material has been taken to a surface disposal site, it is not used later. Storage refers to temporary stockpiling. It can be done when there is no immediate need for the material and a future use is anticipated, or when further pathogen reduction and drying is desired before application.
This technology is primarily used for sludge, although it is applicable for any type of dry, unusable material. One application of surface disposal is the disposal of dry cleansing materials, such as toilet paper, corn cobs, stones, newspaper and/or leaves. These materials cannot always be included along with other water-based products in some technologies and must be separated.
A rubbish bin should be provided beside the User Interface to collect the cleansing materials and menstrual hygiene materials. Dry materials can be burned (e.g., corn cobs) or disposed of along with the household waste. For simplicity, the remainder of this technology information sheet will be dedicated to sludge since standard solid waste practices are beyond the scope of this Compendium.
When there is no demand for or acceptance of the beneficial use of sludge, it can be placed in monofills (sludge-only landfills) or heaped into permanent piles. Temporary storage contributes to further dehydration of the product and the die-off of pathogens before it is used.
Contents
Design Considerations
Landfilling sludge along with municipal solid waste (MSW) is not advisable since it reduces the life of a landfill, which has been specifically designed for the containment of more noxious materials. As opposed to more centralized MSW landfills, surface disposal sites can be situated close to where the sludge is treated, limiting the need for long transport distances.
The main difference between surface disposal and land application is the application rate. There is no limit to the quantity of sludge that can be applied to the surface since nutrient loads or agronomic rates are not a concern. Attention must be paid, however, to groundwater contamination and leaching. More advanced surface disposal systems may incorporate a liner and leachate collection system in order to prevent nutrients and contaminants from infiltrating the groundwater. Sites for the temporary storage of a product should be covered to avoid rewetting by rainwater and the generation of leachate.
| Advantages | Disadvantages/limitations |
|---|---|
| - May prevent unmitigated disposal - Storage may render the product more hygienic |
- Requires a large land area - Potential leaching of nutrients and contaminants into groundwater |
Appropriateness
Since there are no benefits gained from surface disposal, it should not be considered as a primary option. However, where sludge use is not easily accepted, the contained and controlled stockpiling of solids is far preferable to uncontrolled dumping. Storage may, in some cases, be a good option to further dry and sanitize a material and to generate a safe, acceptable product. Storage may also be required to bridge the gap between supply and demand. Surface disposal and storage can be practiced in almost every climate and environment, although they may not be feasible where there is frequent flooding or where the groundwater table is high.
Health Aspects/Acceptance
If a surface disposal and storage site is protected (e.g., by a fence) and located far from the public, there should be no risk of contact or nuisance. The contamination of groundwater resources by leachate should be prevented by adequate siting and design. Care should be taken to protect the disposal or storage site from vermin and pooling water, both of which could exacerbate smell and vector problems.
Operation & Maintenance
Staff should ensure that only appropriate materials are disposed of at the site and must maintain control over the traffic and hours of operation. Workers should wear appropriate protective clothing.
References and external links
- Strande, L., Ronteltap, M. and Brdjanovic, D. (Eds.) (2014). Faecal Sludge Management. Systems Approach for Implementation and Operation. IWA Publishing, London, UK. (Detailed book compiling the current state of knowledge on all aspects related to FSM)
- U.S. EPA (1999). Biosolids Generation, Use, and Disposal in the United States. EPA-530/R-99-009. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D.C., US.
- U.S. EPA (1994). A Plain English Guide to the EPA Part 503 Biosolids Rule. EPA832-R-93-003. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D.C., US.
Acknowledgements
The material on this page was adapted from:
Elizabeth Tilley, Lukas Ulrich, Christoph Lüthi, Philippe Reymond and Christian Zurbrügg (2014). Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies, published by Sandec, the Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries of Eawag, the Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology, Dübendorf, Switzerland.
The 2nd edition publication is available in English. French and Spanish are yet to come.