Difference between revisions of "ഏത്തം"
(Malayalam version of the Article - Counterpoise lift) |
m |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
* [http://publications.iwmi.org/pdf/H015867.pdf Program on Farmer-Managed Irrigation Systems and Support Services]. International Fund for Agricultural Development and the Bundesministerium fur Wirtschaftliche Zusammenarbeit und Entwicklung (BMZ) Government of the Federal Republic of Germany. October 1994. By the International Irrigation Management institute. Colombo, Sri Lanka. | * [http://publications.iwmi.org/pdf/H015867.pdf Program on Farmer-Managed Irrigation Systems and Support Services]. International Fund for Agricultural Development and the Bundesministerium fur Wirtschaftliche Zusammenarbeit und Entwicklung (BMZ) Government of the Federal Republic of Germany. October 1994. By the International Irrigation Management institute. Colombo, Sri Lanka. | ||
* Jane Olley. [http://www.cd3wd.com/cd3wd_40/cd3wd/Practact/KnO-100410-human_animal_water_lifters.pdf HUMAN & ANIMAL POWERED WATER-LIFTING DEVICES FOR IRRIGATION.] Practical Action. November, 2008. | * Jane Olley. [http://www.cd3wd.com/cd3wd_40/cd3wd/Practact/KnO-100410-human_animal_water_lifters.pdf HUMAN & ANIMAL POWERED WATER-LIFTING DEVICES FOR IRRIGATION.] Practical Action. November, 2008. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===This article in other languages=== | ||
| + | [[Counterpoise lift|English]] | ||
Revision as of 09:51, 13 June 2014
( Malayalam version of the Article Counterpoise lift )


Scoop irrigation
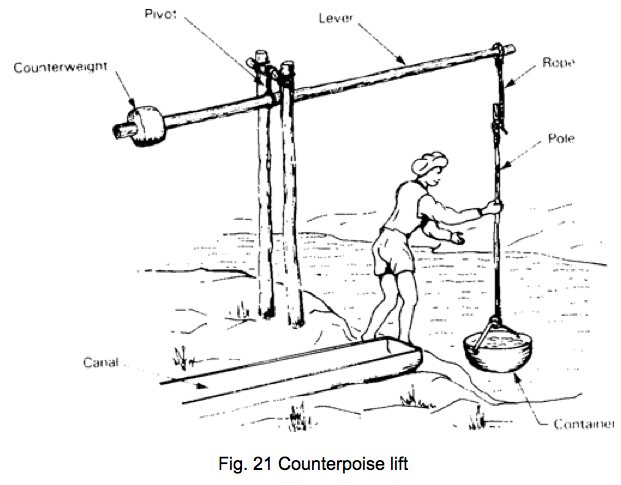
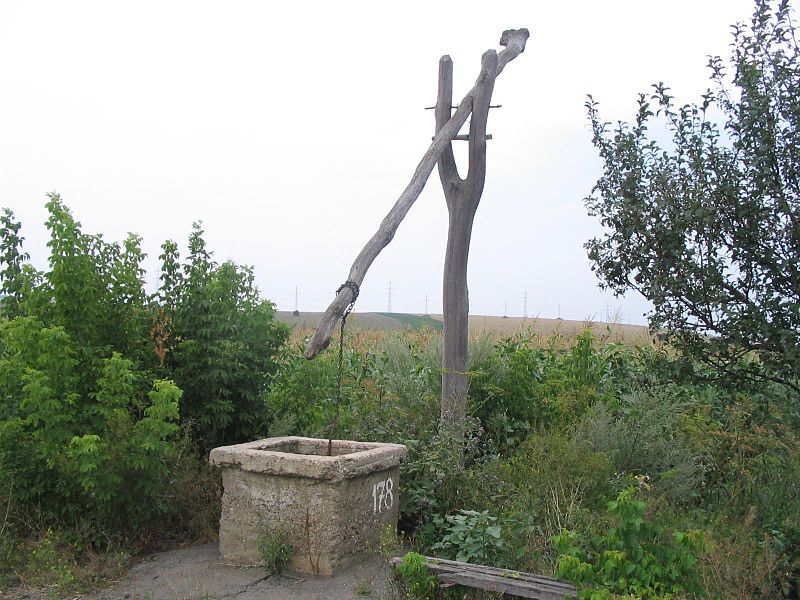
അറബി ഭാഷയില് ഷാഡൂഫ് എന്നും ഹിന്ദിയില് ഡെങ്ക്ലി എന്നും അറിയപ്പെടുന്ന ഏത്തം മരം കൊണ്ടുള്ള ജലസേചനയന്ത്രമാണ്. കിണറുകളില് നിന്നും, തോടുകളില് നിന്നും വെള്ളം മുകളിലേക്ക് ഉയര്ത്തി പാടങ്ങളില് ജലസേചനം ചെയ്യാനുപയോഗിച്ചിരുന്ന സംവിധാനം. മരം കൊണ്ടുള്ള നീളമുള്ള ഒരു തണ്ടിന്റെ ഒരറ്റത്ത് കല്ലോ മണ്ണോ ഭാരമായി തൂക്കിയിട്ടിരിക്കും. മറ്റേ അറ്റത്ത് തൊട്ടി താഴേക്ക് ഇറക്കുന്നതിനായി നീളമുള്ള മുളയോ കമ്പോ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു. ഒരറ്റത്ത് തൊട്ടി കെട്ടിയ മുളവടിയുടെ മുകളറ്റം മരം കൊണ്ടുള്ള തണ്ടുമായി കയറു കൊണ്ട് ബന്ധിച്ചിരിക്കും. വെള്ളം നിറച്ച തൊട്ടി മുകളിലെത്തുമ്പോള് കാലു കൊണ്ട് ഒരു വശത്തേക്ക് ചരിച്ചാണ് വെള്ളം പുറത്തേക്കൊഴുക്കുക. രണ്ടോ മൂന്നോ മീറ്റര് വരെ ആഴമുള്ള കിണറുകളില് നിന്നും മണിക്കൂറില് 2000 ലിറ്റര് വരെ വെള്ളം ഏത്തം ഉപയോഗിച്ച് തേവാനാകും.
പശ്ചിമബംഗാളിലും അയല് സംസ്ഥാനങ്ങളിലും ഉപയോഗിച്ചിരുന്ന ഡോണ് എന്ന ജലസേചന യന്ത്രം ഏത്തത്തിന്റെ മറ്റൊരു രൂപമാണ്. തോണിയുടെ ആകൃതിയില് ഒരു ഭാഗം മൂടിക്കെട്ടി മറുഭാഗം തുറന്നിരിക്കുന്ന വെള്ളത്തൊട്ടിയാണ് ഡോണില് ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നത്. മരവും നാകം പൂശിയ ലോഹത്തകിടുകളും കൊണ്ടാണ് ഈ വെള്ളത്തൊട്ടി നിര്മ്മിക്കുന്നത്. ഇളകാതെ പ്രതിഷ്ഠിതമായ കേന്ദ്രത്തിലൂന്നി ഇരു വശങ്ങളിലേക്കും വെള്ളത്തൊട്ടി ആന്ദോളനം ചെയ്യുമ്പോള് വെള്ളത്തൊട്ടിയുടെ തുറന്ന ഭാഗത്തു കൂടെ വെള്ളം പുറത്തേക്കു പ്രവഹിക്കും.
The pi cottah, used primarily in India, is similar to the shaduf but is operated by two people, one of whom acts as a moving counter weight to eliminate much of the strenuous work of returning the water container against a stationary counter weight. Although it can lift water 5-8 m (16-26 ft), its output is small, and it is used primarily to water small vegetable plots.
Bucket systems may also be adapted to animal power to increase flow, such as with the mohte, or self-emptying bucket. This traditional device employs either a tipping action or simple flap valves in the bucket or bag to discharge the water at lifts of 5-10 m (16-33 ft). The system can be arranged for the animal to walk back and forth in a straight line or in a circle, thus requiring less supervision.
The low-lift dhone, or see-sawing gutters from Bangladesh, can deliver about 300 liters/min (80 gal/min) at a 1 m (3.3 ft) lift. This device uses flap valves and can be operated by a single person shifting the weight back and forth at the fulcrum.
Suitable conditions
The advantage of a counterpoise lift over handpumps is the replacement parts can be acquired locally. Sometimes mechanical handpump parts are more difficult to obtain. They also tend to need a certain amount of preventive maintenance if premature failure of components or impaired performance is to be avoided.1
The counterpoise lift is used extensively in Egypt. It is also common in Nigeria, Southern Niger, and Chad.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| - A relatively inexpensive traditional technology, which can be locally made and maintained. - Easy to operate |
- Limited to lifts of less than 4 m - Limited water yield, 60 l/minute, suitable for small fields |
നിര്മ്മാണ ചെലവ്
ആഫ്രിക്കയിലെ ചാഡില് ഒരു ഏത്തം നിര്മ്മിക്കാന് വേണ്ടുന്ന ഏകദേശ ചെലവ് 40 ഡോളറാണ്. (ഏകദേശം 2,400 രൂപ)
അവലംബം
- ↑ 4. POWER FOR PUMPING, FAO.
Acknowledgements
- Water lifting devices. Agricoop.nic.in
- Food from Dryland Gardens - An Ecological, Nutritional, and Social Approach to Small Scale Household Food Production. CPFE, 1991.
- Program on Farmer-Managed Irrigation Systems and Support Services. International Fund for Agricultural Development and the Bundesministerium fur Wirtschaftliche Zusammenarbeit und Entwicklung (BMZ) Government of the Federal Republic of Germany. October 1994. By the International Irrigation Management institute. Colombo, Sri Lanka.
- Jane Olley. HUMAN & ANIMAL POWERED WATER-LIFTING DEVICES FOR IRRIGATION. Practical Action. November, 2008.